Transactional File Locking¶
ownCloud’s new transactional file locking mechanism operates differently than the old File Locking application, and will eventually replace it. If you elect to use the new file locking mechanism make sure you disable the File Locking app.
The new file locking mechanism has these capabilities:
- Operates at a higher level than the filesystem, so you don’t need to use a filesystem that supports locking
- Locks parent directories so they cannot be renamed during any activity on files inside the directories
- Releases locks after file transactions are interrupted, for example when a sync client loses the connection during an upload
- Manage locking and releasing locks correctly on shared files during changes from multiple users
- Manages locks correctly on external storage mounts
- Manages encrypted files correctly
You must install the Redis server and php-redis module for the new file locking to work. On Debian/Ubuntu/Mint this is redis-server and php5-redis, and on Red Hat/CentOS/Fedora is it redis and php-pecl-redis from the EPEL repository. After installing Redis and its corresponding PHP module, restart your HTTP server.
After installing Redis you must enter a simple configuration in your config.php file, like this example:
'filelocking.enabled' => 'true',
'memcache.locking' => '\OC\Memcache\Redis',
'redis' => array(
'host' => 'localhost',
// can also be a unix domain socket:
'/tmp/redis.sock',
'port' => 6379,
'timeout' => 0.0,
// Optional, if undefined SELECT will not run and will use Redis
// Server's default DB Index.
//'dbindex' => 0,
),
The Server status section on your ownCloud Admin page indicates whether transactional file locking is enabled or disabled.
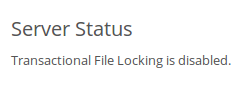
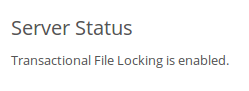
See config.sample.php to see configuration examples for Redis, and for all supported memcaches.
Learn more about Reds at Redis. Memcached, the popular distributed memory caching system, is not suitable for the new file locking because it is not designed to store locks, and data can disappear from the cache at any time. Redis is a key-value store, and it guarantees that cached objects are available for as long as they are needed.